Advancements in AI Reasoning Models: The Next Leap in Machine Intelligence
- Shashank Mishra
- Mar 30, 2025
- 3 min read

New reasoning AI models need fewer parameters to achieve human-like logical thinking, reducing the dependency on massive data centers.
Artificial intelligence is evolving rapidly, and one of the most significant breakthroughs in recent years is the development of advanced AI reasoning models. Unlike traditional AI models that require extensive training on vast datasets, the new generation of reasoning AI models, such as OpenAI's o1 and Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking, can operate with significantly less pre-training and computing power. This innovation is set to revolutionize AI applications across various industries while reducing dependency on massive infrastructure investments.
The Shift Towards Reasoning AI Models
Traditional AI models rely on extensive training using large datasets, requiring substantial computing power and time to process. However, reasoning AI models function differently. Instead of merely predicting outcomes based on pre-trained patterns, these models are designed to mimic human-like reasoning. By analyzing contextual clues and logical structures, they can make informed decisions with less reliance on massive amounts of data.
Key Innovations in AI Reasoning Models

The emergence of reasoning AI models introduces several groundbreaking advancements:
Reduced Computational Costs – Traditional AI models demand powerful GPUs and high-performance cloud computing services, leading to increased costs. Reasoning AI models, with their ability to function with less pre-training, offer cost-efficient solutions for businesses looking to adopt AI without significant financial investments.
Improved Decision-Making – Unlike previous AI models that rely heavily on statistical probabilities, reasoning AI models can analyze data more dynamically, leading to more accurate and nuanced responses.
Faster Adaptability – These models are more flexible in adapting to new data and real-time changes, making them particularly useful for industries requiring rapid decision-making, such as finance, healthcare, and autonomous systems.
Enhanced Generalization Capabilities – AI models traditionally struggle with applying learned knowledge to new, unseen scenarios. Reasoning AI models, however, excel in transferring their logical thinking to new problems with minimal retraining.
OpenAI’s o1 and Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking
OpenAI’s o1 Model
OpenAI’s o1 model is a pioneering effort in reasoning AI. It integrates a lightweight architecture with robust logical reasoning capabilities, enabling it to handle complex decision-making tasks with minimal pre-training. Key benefits include:
Lower hardware requirements, reducing energy consumption and infrastructure costs.
Enhanced real-time reasoning, making it suitable for applications like customer support, legal assistance, and personalized AI interactions.
Greater efficiency in processing unstructured data, such as text, images, and voice commands.
Google’s Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking
AI systems like DeepMind’s Alpha Geometry solve complex mathematical proofs without human assistance, showcasing advanced reasoning.
Google’s Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking is another groundbreaking model focused on improving AI’s cognitive abilities. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on large-scale pattern recognition, Gemini 2.0 introduces:
Context-aware reasoning, allowing it to understand and respond more naturally in conversations.
Smarter decision-making in real-time applications, making it valuable for industries like finance, robotics, and supply chain management.
Higher efficiency with lower training costs, making AI adoption more accessible for businesses of all sizes.
Implications for AI Development and Industry Adoption
The development of reasoning AI models is expected to have profound implications across various sectors:
Enterprise AI Applications – Businesses can leverage AI reasoning models for customer service chatbots, fraud detection, and intelligent data analysis without requiring excessive cloud computing resources.
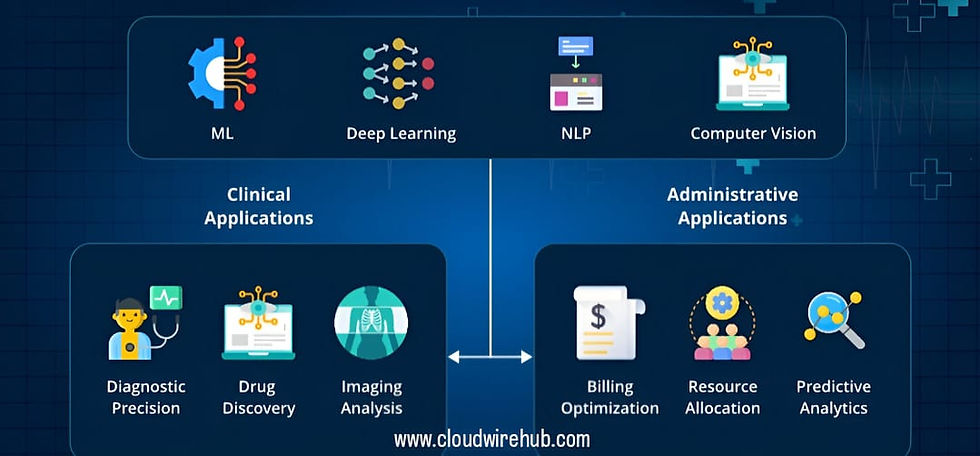
Healthcare Innovations – AI reasoning models can assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately, predicting treatment outcomes, and even suggesting personalized medical plans.
Autonomous Systems – Self-driving cars and smart drones can greatly benefit from AI that can make real-time decisions based on environmental context.
Legal and Compliance Assistance – Legal firms can use AI reasoning models for contract analysis, legal research, and compliance monitoring, reducing time and effort spent on repetitive tasks.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While reasoning AI models offer immense promise, they also present challenges that must be addressed:
Ethical Considerations – As AI models become more autonomous, ensuring transparency and fairness in decision-making will be crucial.
Security Concerns – AI models must be safeguarded against potential misuse or adversarial attacks that could manipulate their reasoning abilities.
Continued Research and Development – Advancing reasoning AI will require ongoing research to improve its contextual understanding and logical capabilities further.
Conclusion

Unlike previous generations, modern AI reasoning models consume less power while maintaining high computational performance.
The rise of reasoning AI models like OpenAI’s o1 and Google’s Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking marks a transformative shift in artificial intelligence. These models not only reduce computational costs but also enhance AI’s ability to make informed, context-driven decisions. As industries increasingly integrate these innovations, the potential for AI-powered advancements across various sectors continues to grow.
By minimizing infrastructure investments and offering smarter, more adaptive AI solutions, reasoning AI models pave the way for a more efficient and accessible future for artificial intelligence. Businesses and researchers must stay ahead of these developments to harness AI’s full potential in reshaping industries and improving everyday life.



Comments